Cats possess a natural and instinctive behavior for hunting, which can be traced back to their ancestral roots as predators. Although domestic cats are primarily kept as pets and provided with food by their owners, their ingrained hunting instincts remain a prominent aspect of their behavior. Understanding cat hunting instincts and how they utilize their hunting techniques can provide valuable insights into their behavior and assist pet owners in addressing any concerns that may arise.
Cats have an inherent prey drive that motivates their hunting behavior. This prey drive is a reflection of their status as obligate carnivores and their adapted traits for hunting small prey like birds and small mammals. Even though domesticated cats receive regular meals from their owners, their hunting instincts persist as an outlet for their prey drive and as a means to meet their unique nutritional requirements.
When hunting, cats follow a specific sequence of behaviors that involve stalking, pouncing, and capturing their prey. They approach their intended target in a crouched position, gradually edging closer until they are within striking distance. With a swift motion, they pounce and use their front paws to secure the prey. While some cats may exhibit variations in their hunting sequence, this general pattern of behavior prevails.
Contrary to popular belief, hunting behavior in cats is not solely driven by hunger. Although hunger can be a motivating factor, cats are opportunistic feeders and will seize hunting opportunities even when well-fed. Hunting is an instinct that is deeply ingrained within them, and they will engage in predatory behavior whenever the opportunity arises. However, hunger does influence whether they will consume the prey they have caught.
Another intriguing aspect of cat hunting behavior is when they bring home prey. This behavior is not necessarily a gift to their owners but rather a reflection of their instinct to provide for their young or family members. It may also be rooted in their desire to consume the prey in the safety and comfort of their home environment.
Play behavior in cats often mirrors their predatory instincts. Through play, cats are able to practice their hunting skills, release pent-up energy, and stimulate their minds. Play also serves as a displacement behavior, allowing cats to express their hunting instincts in a safe environment.
If hunting behavior becomes a concern for pet owners, there are strategies to help reduce it without completely eliminating it. Providing a high-quality, meat-based diet can help satisfy a cat’s nutritional needs and potentially lessen their motivation to hunt. Feeding cats small, frequent meals that mimic their natural feeding patterns, using puzzle feeders or timed feeders, and increasing playtime with hunting-themed toys can redirect their hunting instincts.
It’s crucial to be aware that cats exposed to hunting prey may be at risk of contracting parasites or diseases from their catch. Regular veterinary check-ups, fecal testing, and preventative measures such as flea and tick prevention can help mitigate these risks and safeguard the overall health of the cat.
While discouraging hunting behavior in cats is possible, it’s essential to ensure their overall welfare and consider their natural instincts. Striking a balance between redirecting their hunting behavior and providing appropriate outlets for their instincts allows pet owners to navigate this aspect of their cat’s behavior effectively.
Key Takeaways:
- Cats have natural hunting instincts that stem from their ancestral roots as predators.
- Understanding why cats hunt and how they employ their hunting techniques can provide valuable insights into their behavior.
- Cat hunting behavior is driven by their prey drive, an essential aspect of being obligate carnivores.
- When hunting, cats follow a specific sequence of behaviors, including stalking and pouncing.
- Hunting behavior in cats is not solely motivated by hunger but is deeply ingrained in their instincts.
Why Do Domestic Cats Hunt?
Domestic cats engage in hunting behavior due to their innate hunting instincts and their status as obligate carnivores. These instincts have been passed down through generations of cats, even as they have become domesticated and have their food provided by their owners. Cats are biologically adapted to hunt and consume small prey such as birds and small mammals, and their hunting behavior is crucial for meeting their unique nutritional requirements.
Despite being fed by their owners, cats continue to exhibit hunting behavior because it is deeply ingrained in their nature. Hunting serves as an outlet for their prey drive, allowing them to exercise their natural instincts and behaviors. It gives them a way to express their natural hunting skills and instincts, contributing to their overall well-being and mental stimulation.
Cats have retained their hunting instincts over time because they are obligate carnivores, which means that they require a diet predominantly composed of animal protein. Their bodies are specifically designed for hunting and consuming prey, with sharp teeth and claws for capturing and killing, as well as a highly developed sense of hearing and sight to locate and track potential prey.
How Do Domestic Cats Hunt?
Domestic cats have a specific sequence of behaviors they follow when hunting prey. This sequence typically involves stalking, pouncing, and capturing the prey. Cats usually approach their prey in a crouched position, slowly moving closer until they are within striking distance. Once they are close enough, they will spring forward and use their front paws to capture the prey.
Stalking and pouncing are key hunting techniques in domestic cats. Their stealthy stalking allows them to get close to their prey without alerting it, and their swift pouncing ensures a successful capture. Cats are highly skilled at coordinating their movements to execute the hunt effectively.
The cat hunting sequence may vary slightly depending on the individual cat and its hunting expertise. Some cats may exhibit more patience in stalking, while others may rely more on their agility and speed during the capture phase. Regardless of the variations, the underlying instinct and behavior remain consistent.
Predatory Sequence:
- Stalking: Cats move silently and deliberately, keeping their body low to the ground to stay hidden from their prey.
- Pouncing: Once the cat is within range, it will use its powerful hind legs to launch itself forward with precision and speed.
- Capture: Cats use their front paws to grab and immobilize their prey, typically targeting the head or neck area.
It’s important to understand the hunting techniques employed by domestic cats to better comprehend their behavior and address any concerns related to their hunting instincts. By acknowledging these natural instincts, pet owners can provide appropriate outlets for their cat’s predatory behavior, such as interactive toys that mimic prey movement.
Is Hunting Always Motivated by Hunger?
While hunger can certainly motivate hunting behavior in cats, it is important to note that hunting is not solely driven by their need for food. Cats are opportunistic feeders, and they will seize hunting opportunities even when they are not hungry. This behavior is deeply ingrained in their instinct as predators, and they will engage in hunting whenever the chance arises, regardless of their hunger levels.
Cats rely solely on themselves for food and cannot depend on consistently finding prey when they are hungry. Therefore, they take advantage of any hunting opportunities that present themselves to ensure their survival. Even well-fed cats will continue to engage in hunting behavior because it is an integral part of their nature.
However, hunger does play a role in whether a cat will consume the prey they have captured. When cats are hungry at the time of the hunt, they are more likely to kill and consume the prey. This is because hunger enhances their motivation to satisfy their nutritional needs. Cats instinctively recognize when they are in need of sustenance and will take advantage of a successful hunt.
To summarize, while hunger influences the prey kill and consumption aspect of hunting behavior, cats will still engage in hunting regardless of their hunger levels. Hunting opportunities are seen as a way to thrive and maintain their natural instincts as predators, ensuring their well-being even when food is readily available.
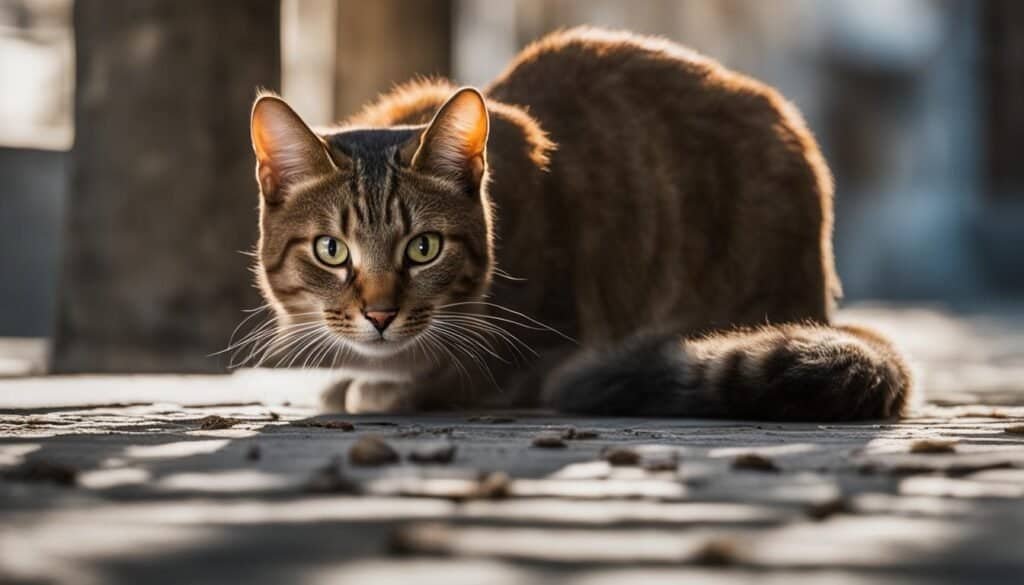

Why Do Cats Bring Home Prey?
When it comes to cats bringing home prey, it’s not always a gesture of gift-giving towards their owners. Instead, this behavior is deeply rooted in their natural instincts as hunters and their drive to provide for their young or family members. Cats may perceive their owners as part of their close-knit family and feel compelled to share their catch as a means of care and provision. This prey-sharing behavior is an instinctive way for cats to show their nurturing side and ensure the survival of their loved ones.
“Cats may consider their owners as part of their family and bring home prey as a way to provide and care for them.”
Additionally, cats may bring home prey with the intention of consuming it later in the safety and comfort of their home environment. By bringing the prey home, they ensure a secure location for consuming their catch without the threat of predators or other interruptions. This behavior further demonstrates their resourcefulness and adaptation to their domestic surroundings while still preserving their innate hunting instincts.
Understanding the reasons behind a cat bringing home prey is vital for interpreting and responding appropriately to this behavior. It allows pet owners to recognize and appreciate the natural instincts and intentions behind their feline companion’s actions. Instead of perceiving it as a gift, it should be acknowledged as an expression of their hunting prowess and their desire to provide and care for their family, which includes their human owners.
The Relationship Between Play and Predation
Cats are known for their inherent hunting instincts, which they often express through play behavior. Whether it’s chasing after a toy or pouncing on a small object, cats engage in play that closely resembles hunting. This serves multiple purposes for our feline friends.
- Practice Hunting Skills: Play allows cats to develop and refine their hunting techniques. Through play, they can sharpen their stalking, pouncing, and capturing abilities. It’s like a training ground for their natural instincts.
- Mental and Physical Stimulation: Play behavior provides cats with both mental and physical exercise. It keeps their minds sharp and their bodies active, helping to prevent boredom and promote overall well-being.
- Release of Predatory Instincts: Play allows cats to satisfy their predatory instincts in a safe and controlled environment. It provides an outlet for their natural hunting instincts, preventing them from becoming frustrated or bored.
Cats may also engage in play as a form of displacement behavior. This means that play serves as a diversion from their natural hunting instincts when they are unable to engage in actual hunting. By providing a substitute for real prey, play helps cats release their pent-up energy and frustration.
Understanding the connection between play and predation is vital for cat owners. By recognizing that play is not just a source of entertainment but also a crucial aspect of a cat’s life, we can provide appropriate outlets for their hunting instincts. Toys designed to mimic prey, such as interactive wand toys or puzzle feeders, can give cats the opportunity to express their hunting behavior in a safe and stimulating way.
“Play behavior serves as an important outlet for a cat’s hunting instincts and allows them to satisfy their natural predatory needs while keeping them physically and mentally engaged.” – Dr. Emily Jones, Feline Behavior Specialist
To further illustrate the relationship between play and predation, consider the image below:
As shown in the image, play behavior closely mirrors the hunting behavior observed in cats. From stalking to chasing and pouncing, play provides cats with a platform to simulate and refine their hunting skills.
Can Hunting Behavior Be Reduced?
While hunting behavior is natural for cats, there are strategies that pet owners can employ to help reduce it if it becomes a concern. By understanding the underlying reasons behind a cat’s hunting instincts, cat owners can implement behavior modification techniques and provide alternative outlets for their cat’s natural hunting behavior.
To reduce hunting behavior in cats, it is important to address their nutritional needs. Providing a highly palatable cat food with a high meat content can help satisfy their nutritional requirements, potentially reducing their motivation to hunt. Feeding cats small, frequent meals throughout the day and using puzzle feeders or timed feeders can mimic their natural feeding patterns and provide mental stimulation, which can help divert their attention away from hunting.
Increasing playtime with cats using toys that resemble prey can also redirect their hunting instincts. Interactive toys such as fishing rod toys or laser pointers can engage their predatory behavior and provide an outlet for their hunting instincts in a safe and controlled manner.
It’s important to note that completely eliminating hunting behavior in cats is not recommended, as it is an innate feline behavior and eliminating it can compromise their welfare. Hunting behavior provides mental and physical stimulation for cats and allows them to engage in their natural instincts. Instead of eliminating hunting behavior entirely, the goal should be to redirect and manage it appropriately.
By implementing these strategies, pet owners can help reduce hunting behavior in cats while still respecting their natural instincts. It is important to remember that every cat is different, and what works for one cat may not work for another. Observation, patience, and understanding are key when modifying cat behavior.
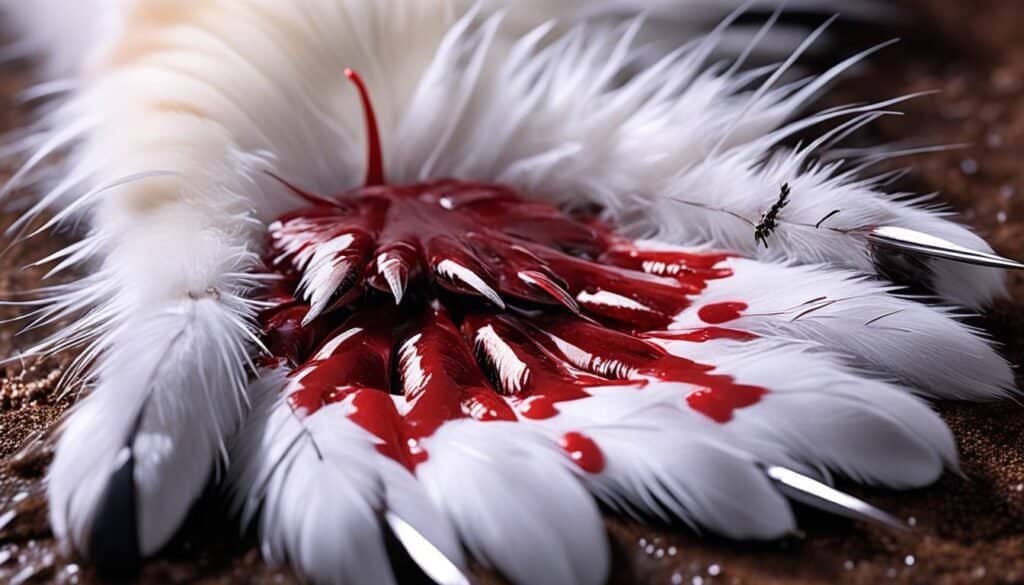
The Health Risks of Cat Hunting
Cats that engage in hunting behavior are exposed to various health risks associated with their prey. When cats hunt and capture wild animals, there is a chance of contracting intestinal parasites such as roundworms. These parasites can be transmitted to cats during a hunt and can pose a risk to their overall health.
Another potential health risk for hunting cats is the transmission of diseases like toxoplasmosis. Cats can become infected with toxoplasmosis from consuming infected prey. Toxoplasmosis can then be transmitted to humans, particularly those with weakened immune systems, pregnant women, and young children.
It is crucial for pet owners to be aware of these health risks and take necessary precautions when handling or disposing of prey. Regular fecal testing for parasites can help identify and address any potential infestations early on. Additionally, preventative measures such as flea and tick prevention can reduce the risk of transmission.
“Cats that engage in hunting behavior are exposed to health risks associated with their prey.”
To ensure the well-being of both cats and their human companions, responsible cat owners should stay informed about the health risks associated with hunting behavior and take appropriate measures to mitigate those risks.

How to Discourage Hunting Behavior
Pet owners have various options to discourage hunting behavior in their cats. Here are some strategies you can try:
1. Keep cats indoors
Keeping your cat indoors eliminates their access to live prey and reduces the associated risks. By creating an enriched indoor environment with plenty of toys and climbing structures, you can provide mental and physical stimulation for your cat while minimizing their hunting instincts.
2. Create a safe outdoor space
If you want your cat to experience the outdoors without the hunting behavior, consider creating a safe outdoor space like a catio. A catio is an enclosed area that allows your cat to enjoy the sights, sounds, and fresh air while preventing them from hunting wildlife.
3. Use a GPS tracker
If you allow your cat to have supervised outdoor time, using a GPS tracker can help you keep track of their whereabouts and ensure they don’t roam too far. This way, you can have peace of mind knowing that your cat is safe and under your watchful eye.
4. Redirect hunting instincts through play
Offering alternative outlets for your cat’s hunting instincts is essential. Engage your cat in interactive play sessions with toys that resemble prey. This not only provides mental stimulation but also satisfies their instinctual need to hunt. Try experimenting with different toy styles, such as feather wands or treat-dispensing puzzles, to find what captivates your cat’s interest.
By implementing these strategies, you can help discourage hunting behavior in your cat while providing a safe and stimulating environment for them to thrive.
Conclusion
Cat hunting instincts are a natural part of their behavior as predators. Understanding the reasons behind their hunting behavior is crucial for cat owners to provide appropriate care and manage their instincts effectively. While it is impossible to completely eliminate hunting behavior, there are strategies that can be employed to redirect and control it.
One key approach is to provide ample opportunities for play. Engaging cats in interactive play with toys that resemble prey helps satisfy their hunting instincts and provides mental and physical stimulation. Additionally, incorporating feeding patterns that mimic their natural hunting behaviors, such as small, frequent meals or puzzle feeders, can help divert their focus from hunting.
Moreover, making environmental modifications in the form of safe outdoor spaces, such as catios, can allow cats to experience the outdoors while preventing them from hunting wildlife. For those with outdoor cats, using GPS trackers can provide peace of mind and ensure their cats do not roam too far.
By implementing these strategies and providing proper supervision, cat owners can successfully manage their cats’ hunting instincts and promote a harmonious relationship between their pets and the environment. Remember to always consider your cat’s natural instincts when caring for them, ensuring their well-being while embracing their inherent predator nature.
FAQ
Why do cats hunt?
How do domestic cats hunt?
Is hunting always motivated by hunger?
Why do cats bring home prey?
What is the relationship between play and predation in cats?
Can hunting behavior be reduced in cats?
What are the health risks of cat hunting?
How can hunting behavior be discouraged in cats?
What should pet owners understand about cat hunting instincts?
Last modified: February 20, 2024













[…] incorporating puzzle toys that require problem-solving skills and encourage their natural hunting instincts. Providing climbing structures or a cat tree can also help satisfy their need for vertical […]
[…] kicker toy that your cats will absolutely adore. Not only is it a great way to engage their natural hunting instincts, but it also makes use of catnip, which adds an extra level of excitement to […]
[…] insights into cat behavior modification strategies and feline socialization […]